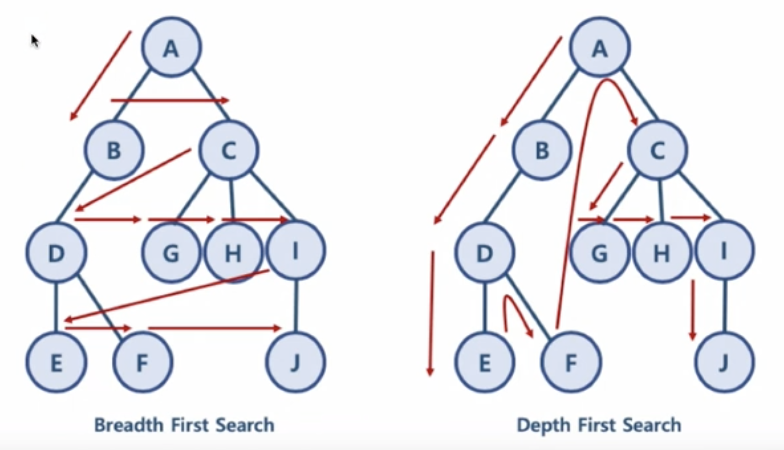
문제 제목 : DFS와 BFS
난이도 : 하
문제 유형 : DFS, BFS
추천 풀이 시간 : 30분 (못하면 2배 60분)
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1260
1260번: DFS와 BFS
첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000), 간선의 개수 M(1 ≤ M ≤ 10,000), 탐색을 시작할 정점의 번호 V가 주어진다. 다음 M개의 줄에는 간선이 연결하는 두 정점의 번호가 주어진다. 어떤 두 정점 사
www.acmicpc.net
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static Integer n, m, v;
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adjList = new ArrayList<>();
public static boolean[] visited = new boolean[1001];
public static void addEdge(int n, int m) {
adjList.get(n).add(m);
}
public static void dfs(int node) {
if (visited[node]) return;
visited[node] = true;
System.out.print(node + " ");
for (int i = 0; i < adjList.get(node).size(); i++) {
dfs(adjList.get(node).get(i));
}
}
public static void bfs(int node) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue.offer(node);
visited[node] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int now = queue.poll();
System.out.print(now + " ");
for (int i = 0; i < adjList.get(now).size(); i++) {
int adjNode = adjList.get(now).get(i);
if (!visited[adjNode]) {
queue.offer(adjNode);
visited[adjNode] = true;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
v = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {
adjList.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
addEdge(x, y);
addEdge(y, x);
}
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++) {
Collections.sort(adjList.get(i));
}
dfs(v);
System.out.println();
visited = new boolean[1001];
bfs(v);
}
}'Algorithm > BAEKJOON' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘-DFS,BFS] 바이러스 (0) | 2023.01.24 |
|---|---|
| [알고리즘-BFS] 숨바꼭질 (0) | 2023.01.24 |
| [알고리즘-DP] 가장 높은 탑 쌓기 (0) | 2023.01.23 |
| [알고리즘-DP] 기타리스트 (0) | 2023.01.23 |
| [알고리즘-DP] LCS (0) | 2023.01.21 |